As a Linux system administrator, to transmit data from
server to server having a good command over the TCP (Transmission
Control Protocol) protocols is very much crucial. In the term of
TCP, we get the idea of two types of ports: Open port and Close
port. In-network transmission control protocol, all the ports which
have accepted transmission of data are called open port, and on the
other hand, the ports where data packets are filtered or couldn’t
reach are called close port. Those who have been working with
Ubuntu server management must know the havoc of not maintaining
networks open ports properly. The knowledge between the open port
and close port is pretty vice versa. In the Linux networking
system, understanding the concept of open ports and checking the
available number of open ports is vital.
Checking Open Ports
in Linux
Network ports are usually allocated just after the IP
address. Let your network address followed by a 16-bit socket, then
the total number of available ports will be 2^16= 65536. In
computer networking, we all are familiar with the concept and types
of networking addresses like physical address and local
address.
Every networking address has an endpoint that defines the
work-type of that network address. Let, we want to send an email
from our Gmail account; in this case, Gmail uses the SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer
Protocol)[1] system. We know that SSL
(Secure Sockets Layer) is a socket number used for identification
and security purpose.
In a word, this socket is called port. For Gmail, the
default SSL or port is 465. The internet service provider(ISP)
often allows its users to download movies of games from their
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) server.
Most of the time, FTP servers are made with Apache Ubuntu server
tools, where ports are kept open and associated with IP addresses.
In the entire post, we cover up the method of how to check open
ports in Linux as well as in Ubuntu.
[2]
| Port Range | Category |
|---|---|
| 0 – 1023 | System Ports |
| 1024 – 49151 | User Ports |
| 49152 – 65535 | Dynamic Ports |
1. Checking Open Ports Using
nmap Command in Linux
In Linux, Network Mapper or nmap command[3] is used for checking the
status of a system, used devices, checking current network
services, and the availability of socket or ports. If your Linux
system doesn’t have nmap installed, for Ubuntu and
other Linux versions, you can install nmap by the
following terminal commands. You can also check the version of your
network mapper.
$ sudo apt-get install nmap $ nmap --version
After the nmap is installed, at the very
first step, we can check the ports of our localhost address. Most
of the time, the localhost IP address is assigned by
127.0.0.1
$ sudo nmap -sT -O localhost
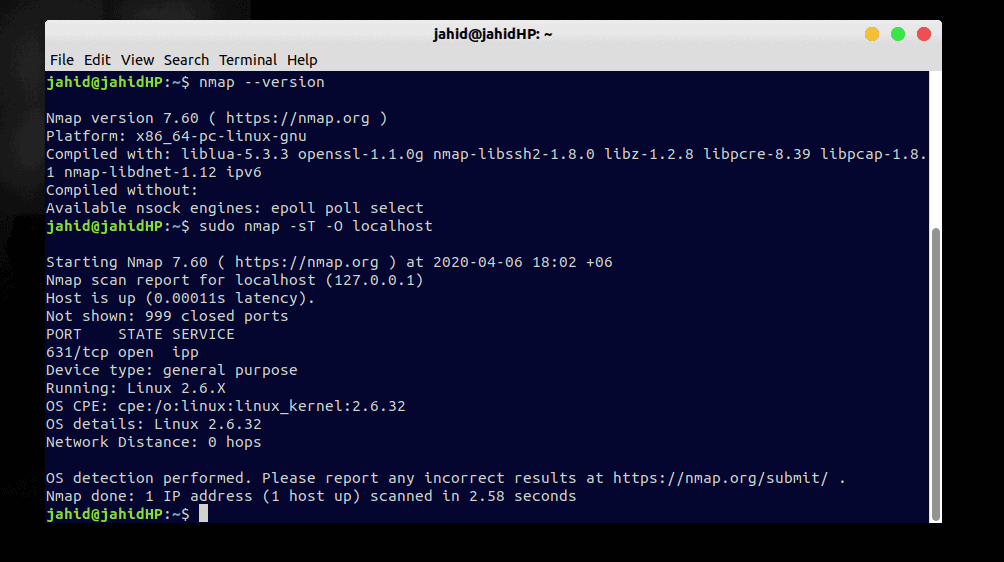
We can also find the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
ports using the nmap command. The namp
command is also used for finding the available ports for a
particular IP Address. Let we want to check the ports for the IP
192.168.0.1
$ sudo nmap 192.168.0.1 $ nmap -open 192.168.0.1 $ nmap google.com
2. Finding Open Ports Using
netcat Command in Ubuntu
Previously we have seen how to check available ports using
Transmission Control Protocol. Now we will see how to check the
available number of ports using the User Datagram Protocol (UDP)[4].
In the Ubuntu server, this kind of networking operations
is done by using the nc or netcat
command. And I must say that in Linux, the netcat is
the most powerful weapon to check network sockets. Let you want to
create a connection under a TCP protocol where the port is assigned
as 2389.
Now you can run the following terminal command to create a
TCP connection. Or, if you are the client, you have access to the
localhost; you can run the second terminal command too.
$ nc -l 2389 $ nc localhost 2389
3. Finding Open
Ports Using netstat Command in
Linux
If you want to check only the UDP User Datagram Protocol
ports, you can also use the network statistics or
netstat command. The netstat command can
display both receiving and sending end transmission data. Finally,
we have one command that can find open ports in Linux by
netstat.
$ netstat --listen $ netstat -lntu $ netstat -vaun
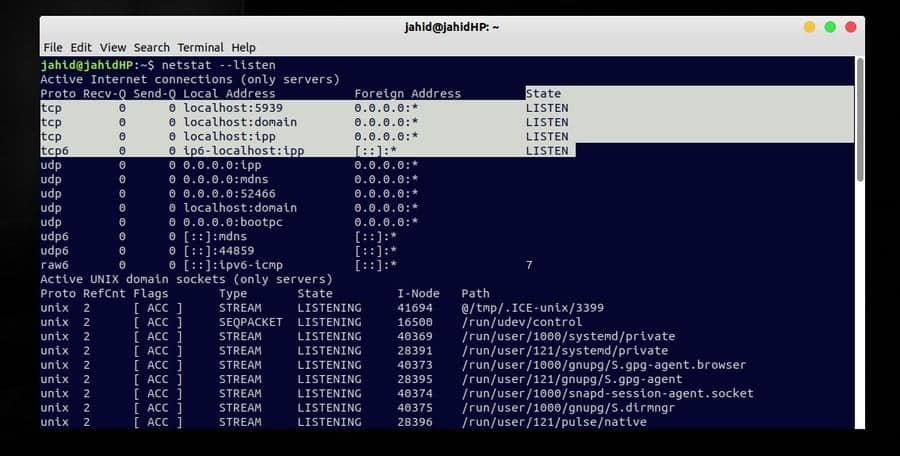
The NGINX command[5]
is also used to monitor the networking system of your Linux. Here
I’m introducing you with a nignx command that can
check the open ports of your Linux system.
$ sudo netstat -lntup | grep "nginx"
If you find the nignx is not working
correctly, try reloading the nignx[6].
$ sudo nginx -t $ sudo nginx -s reload
To find all the open ports in your Linux system, you can
use this terminal command.
$ netstat -antplF
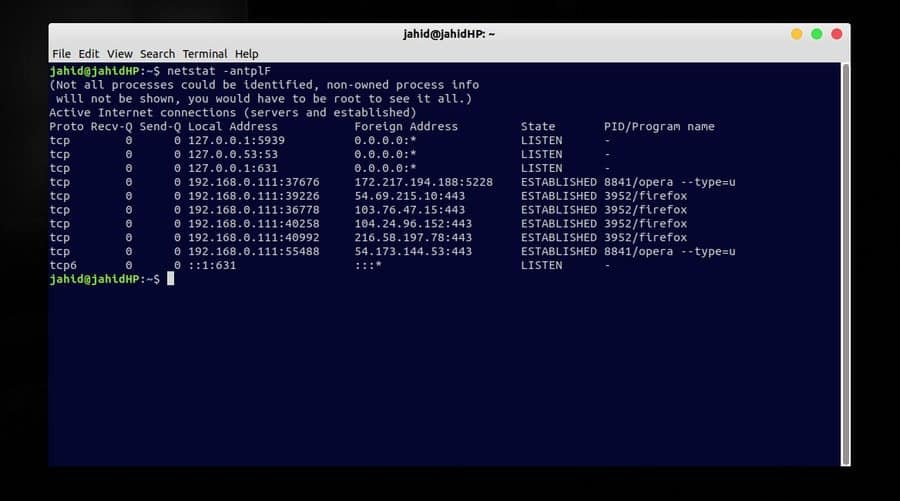
For finding the specific port status in Linux, there is a
netstat command which can display all listening ports.
Let, our specific port is 80.
$ sudo netstat -lntup | grep ":80"
4.
Monitor Listening Ports Using lsof Command in
Ubuntu
In Linux, a list of open files or in short lsof command is used to see the list of
files or directories which are open. But we can also use the
lsof commands for some simple networking tasks. We can
find the list of all open ports by lsof commands. I
must mention that in Linux, open port is also aliased by listening
port.
[7]
Let, we want to check the connected foreign addresses and
the listening ports using the lsof command. Here,
listening or listen is referred to as open ports. In the terminal,
we can use exact data text grabber or Global regular expression
print or, in short, the grep command.
$ lsof -i $ sudo lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN $ lsof -i TCP| fgrep LISTEN
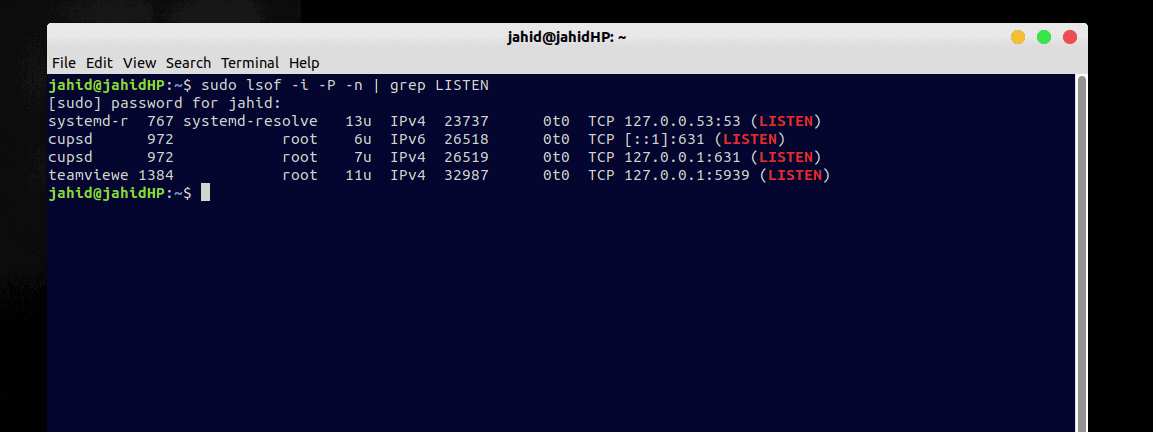
If you want to check the status of a specific port against
an IP address of the network, you can use this terminal command in
your Linux system. Let, we want to check the status for the port
80.
$ sudo lsof -i :80
5. Finding
Established Ports Using ss Command in
Linux
In Linux, the ss command is referred to the
term socket statistics. Here the sockets are assigned
as ports. So by using the ss command, we can determine
the open ports in the Linux system. If you don’t have
ss installed in your Linux, you can quickly install
ss in your machine from the apt command
given below. Then run the sockstat command in your
terminal. In the output, you will find the socket/port
details.
$ sudo apt install sockstat
$ sockstat
$ netstat -an |grep LISTEN
For more informative open port checking purposes, there is
a lntu command in Linux. The lntu command
mainly looks for the details of TCP open ports, UDP open ports,
name of the software, and used port number.
$ ss -lntu
Final
Thoughts
For networking, open ports can be checked by using C++ or
PHP, but the best way to check all open or listening ports is to
use the Linux command lines. These will make
your time efficient. In this post, we have tried to show some
dynamic methods of checking open ports of the Linux system. In some
Linux distributions like Ubuntu and Red Hat, checking open ports
and close ports are unavoidable for firewall security purposes. You can find
SMTP ports, Network Time Protocol (NTP) ports, HTTP ports, and UDP
ports using the commands described above.
[8][9]
The entire post was all about how ports are assigned with
IP addresses and why you can check the open or closed ports in your
Linux system. If you find this post useful, please let us know what
you’ve loved in this post. And you can also write a comment about
this post. Feel free to share this post among your Linux
geeks.
References
- ^
Top 20
Best Linux Mail Server Software and Solutions in 2020
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
Best
Linux FTP Client: Top 10 Reviewed for Linux Geeks
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
50
Essential Nmap Commands for System Admins
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
User
Datagram Protocol (UDP) (en.wikipedia.org) - ^
25 Must
Know Nginx Commands for Developers and Admins
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
20
Essential Things to Know if You’re on Nginx Web Server
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
lsof
command (www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
The 50
Most Useful Linux Commands To Run in the Terminal
(www.ubuntupit.com) - ^
The 15+
Linux Firewall Software For Protecting Your Linux System
(www.ubuntupit.com)
Read more https://www.ubuntupit.com/how-to-check-all-the-open-ports-in-your-linux-system/
